UPSC Current Affairs
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
||||||||||||||||||
| Polity and Governance | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Syllabus:
Preliminary Examination: Indian Polity and Governance – Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues Mains Examination: General Studies-II: Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein. Why in the news: The government introduced two Bills in the Lok Sabha Tuesday as part of its plans for simultaneous elections across the country, countering the Opposition’s charge of the move being “anti-constitutional” and “undermining federal structure”. The Constitution (One Hundred and Twenty-Ninth Amendment) Bill and Union Territories Laws (Amendment) Bill were approved by the Cabinet, recently. Key Points to Study: • What is the process of passing the Constitutional Amendment Bill? • How constitutional amendment bill is different from an ordinary bill? • What is the basic structure doctrine and how the Supreme Court judgments have defined it? • What is the purpose of the Joint Parliamentary Committee? • What is the role of the Election Commission of India in conducting simultaneous elections? • What are the arguments in favour and against the One Nation, one election? Key Takeaways: • The Union Cabinet last week approved the Constitution Bill, and the Union Territories Laws (Amendment Bill), 2024 that would allow holding simultaneous elections to the Lok Sabha as well as state and Union Territory assemblies. The latter seeks to align the elections of the Union territories of Jammu and Kashmir, Puducherry and the NCT of Delhi. • In September 2023, a high-level committee chaired by former President Ram Nath Kovind, to suggest ways and amendments to enable simultaneous elections, had submitted its report. Of the 47 parties that submitted their opinion on the matter to the Kovind panel, 32 supported the idea and 15 opposed it. • As per the draft, the President would have to notify an “appointed date” on the first sitting of the Lok Sabha after a general election, and any Legislative Assembly elected after that date would have its term curtailed to end with that of the Lok Sabha. What are the key takeaways from the two Bills? • First, simultaneous polls, as of now, are only for Parliament and state Assemblies, and not municipal corporations. • Second, these changes can in ordinary circumstances take shape earliest in the 2034 election cycle. The Constitution amendment Bill states that the “President may by a public notification issued on the date of the first sitting of the House of the People after a general election, bring into force the provision of this article, and that date of the notification shall be called the appointed date”. • The earliest date of the first sitting of Lok Sabha will be in 2029, and the next election cycle will be in 2034, assuming that both the 18th and 19th Lok Sabhas complete their full five-year terms. • For the Constitutional amendment to pass in Parliament will require a “special majority” in both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. Two conditions have to be satisfied under Article 368 of the Constitution which gives the power to amend. • First, half of both Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha must vote in favour of the amendment. Second, of all the members “present and voting”, two-thirds must vote in favour of the amendment. • It is practical to leave out municipal elections at this stage. That would have required an amendment to be “ratified” (agreed to) by the legislatures of at least half of all states in the country. • The first Bill is The Constitution (One Hundred and Twenty-Ninth Amendment) Bill, 2024, which proposes to amend three articles of the Constitution and insert a new one, Article 82A(1-6). • This new provision is intended to facilitate the transition to simultaneous elections. It is proposed to be added after Article 82, which pertains to delimitation, which is the readjustment of allocation of Lok Sabha seats among states after every decadal Census. • According to the Bill, Article 82A provides for simultaneous elections to Lok Sabha and state Assemblies. • Under Article 82A(3), the Election Commission of India (ECI) “shall conduct general elections to the House of the People and all Legislative Assemblies simultaneously”. • Article 82 A(4) defines simultaneous elections as “general elections held for constituting the House of the People and all the Legislative Assemblies together”. • Article 82A(5) gives the ECI the option of not holding any particular Assembly election along with the election to Lok Sabha. • Article 82A(6) says if an Assembly election is deferred, the full term of that Assembly will also end with the full term of the Lok Sabha elected in the general election. • For state Assemblies, amendments similar to those proposed to Article 83 are proposed to Article 172, which provides for the duration of state legislatures. • In case of dissolution of a state Assembly before its full term, the election would be held for the unexpired term of the preceding Assembly. • The second Bill, The Union Territories Laws (Amendment) Bill, 2024, has proposed amendments to the Government of Union Territories Act, 1963, the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi Act, 1991, and the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Previous year UPSC Prelims Question Covering similar theme:
(1) Consider the following statements: (2017) 1. The Election Commission of India is a five-member body. 2. The Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and bye-elections. 3. Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognised political parties. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 3 only Ans: d |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
People for Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA) India has called on the neighbouring country's Prime Minister, KP Sharma Oli, to take decisive action to halt mass slaughter of animals during the Gadhimai Festival from December 7 to 9. Key Points: Celebrated every five years, this year's edition will take place at the Gadhimai Temple in Bara District. The festival, famous for animal sacrifice, is one of the largest and most controversial slaughter events. It ranks as one of the world’s largest animal sacrifice festivals, drawing thousands of devotees from Nepal, India, and beyond. The practices, which involve the mass decapitation of animals, expose butchers, temple workers, and attendees to pathogens, potentially triggering outbreaks of zoonotic diseases such as avian influenza, anthrax, and leptospirosis. Supreme Court Rulings: India (2014): The Supreme Court ordered that neighboring Indian states restrict the transport of animals for the Gadhimai festival. Nepal (2016): The Supreme Court ruled that the government should phase out and discourage animal sacrifices. However, this ruling has been largely ignored, and the sacrifices continue. IN SHORT: Gadhimai festival is celebrated every 5 years in Nepal's Bara district Peta India urges Nepal PM KP Sharma Oli to stop animal sacrifice Cites risks posed by slaughter to public health, animal welfare, environment |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Useful information for all competitive exams:
Nepal: Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. Capital: Kathmandu President: Ram Chandra Poudel (3rd President of Nepal) Currency: Nepalese rupee (Rs, रू) (NPR) |
||||||||||||||||||
| International Relations | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
Moldova has officially joined the International Solar Alliance (ISA), signaling its commitment to renewable energy and sustainability. The ISA Framework Agreement was signed in New Delhi by India’s External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar and Moldovan Deputy Prime Minister Mihai Popșoi. Moldova’s inclusion comes after Armenia became the 104th full member last month, marking the continued global expansion of the ISA. Key Points: International Solar Alliance (ISA) Framework Agreement (FA) entered into force in 2017. With amendment of its FA in 2020, all member states of UN are now eligible to join ISA. 7th Session of ISA: The 7th Session of the International Solar Alliance (ISA), which was held in New Delhi from November 3 to 6, 2024, focused on accelerating solar energy deployment across its Member Countries, particularly in regions with limited energy access. During this session, several significant initiatives, programs, and funding schemes aimed at supporting solar energy projects and fostering global cooperation were presented and discussed. About International Solar Alliance (ISA): HQ: Gurugram, India Genesis: Conceptualized on sidelines of COP21 in Paris in 2015. Aim: Collaborative initiative between India and France aimed at uniting efforts to combat climate change by implementing solar energy solutions. Mission: ISA is guided by ‘Towards 1000’ strategy, aiming to: Mobilize USD 1,000 billion of investments in solar energy by 2030. Delivering Energy access to 1,000 million people. 1,000 GW of solar energy installation. ISA Assembly: Apex decision-making body. It plays a key role in shaping and overseeing implementation of ISA's Framework Agreement. Membership: 105 Member countries and 16 signatories’ countries. Objective: The focus is on solar power utilization. The launching of such an alliance in Paris also sends a strong signal to the global communities about the sincerity of the developing nations towards their concern about climate change and to switch to a low-carbon growth path. India has pledged a target of installing 175 GW of renewable energy of which 100 GW will be solar energy by 2022 and reduction in emission intensity by 33–35% by 2030 to let solar energy reach to the most unconnected villages and communities and also towards creating a clean planet. |
||||||||||||||||||
| Economy | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
India’s busiest flight route—Mumbai-Delhi—has been ranked as the eighth busiest domestic route globally in the 2024 rankings released by international aviation and travel data and analytics firm OAG. Within the Asia Pacific region, the Mumbai-Delhi route was ranked as the sixth busiest. 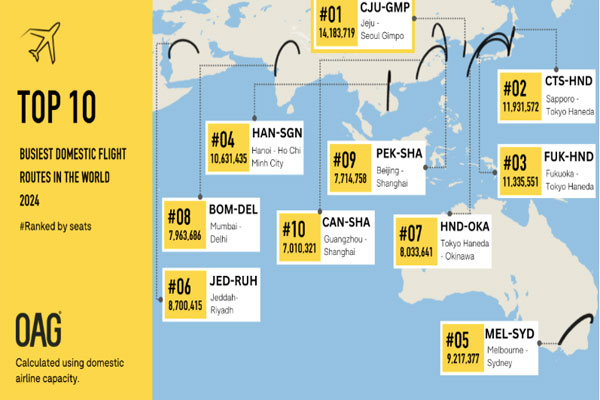 TOP 10 BUSIEST DOMESTIC FLIGHT ROUTES OF 2024: India is the world’s third-largest domestic aviation market, and also among the fastest-growing major aviation markets globally. The Jeju International-Seoul Gimpo route in South Korea, with a seat capacity of 14.18 million in 2024, maintained its position as the busiest domestic flight route in Asia Pacific as well as globally. In fact, the top five domestic routes globally in 2024 were the same as last year. The Asia Pacific region dominated the list of the 10 busiest domestic flight routes in the world for 2024. The list includes three routes from Japan, two from China, and one each from India, South Korea, Vietnam, Australia, and Saudi Arabia. 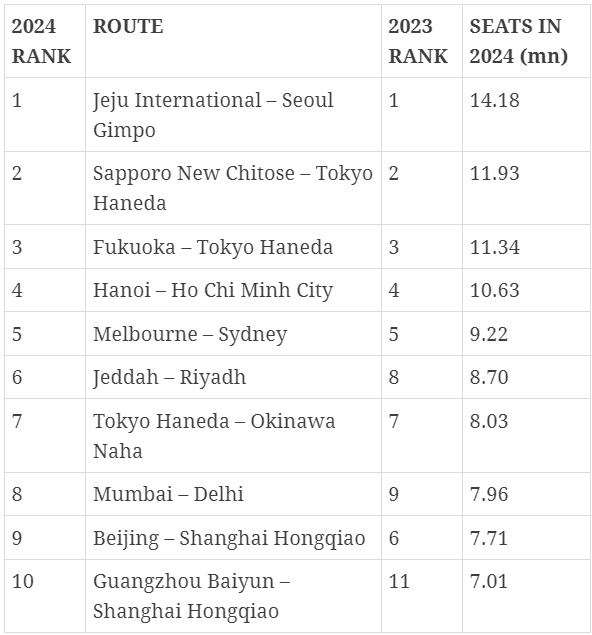 No route from India in top international routes: The Asia Pacific region also dominated the list of the top 10 busiest international routes, although none of those routes were to or from India. The title of the busiest international flight route in 2024 went to Hong Kong-Taipei, which was ranked at the third spot in 2023, per OAG’s rankings. Kuala Lumpur-Singapore, which was ranked the busiest international route last year, slipped to the fourth spot in the 2024 rankings. 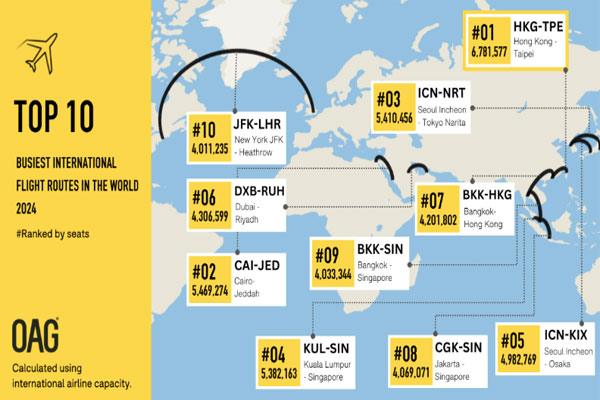 Other top international flight routes included: Cairo-Jeddah (second spot), Seoul Incheon-Tokyo Narita (third spot), Seoul Incheon-Osaka Kansai (fifth spot), Dubai-Riyadh (sixth spot), Bangkok-Hong Kong (seventh spot), Jakarta-Singapore (eighth spot), Bangkok-Singapore (ninth spot), and New York JFK-London Heathrow (tenth spot). |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Useful information for all competitive exams:
OAG (company): OAG is a global travel data provider with headquarters in the UK. Founded: 1929 Headquarters: Luton, England CEO: Phil Callow Parent: Vitruvian Partners |
||||||||||||||||||
| Science and Technology | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
India’s space exploration program reached a pivotal milestone as Isro commences the assembly of the Human-Rated Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (HLVM3) at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), marking the start of the Gaganyaan-G1 launch campaign. Key Takeaways: The mission, scheduled for 2025, will be the first uncrewed flight under the ambitious Gaganyaan human spaceflight program. The event coincides with the 10th anniversary of the LVM3-X/CARE mission, conducted on December 18, 2014. The 2014 mission demonstrated critical technologies for human spaceflight, including the successful launch and recovery of a Crew Module. During that mission, the LVM3-X lifted a 3,775 kg Crew Module to a suborbital altitude of 126 km, followed by a controlled re-entry and splashdown in the Bay of Bengal. These achievements laid the groundwork for the Gaganyaan program, officially approved in 2019. The HLVM3, an evolution of the LVM3, has been specifically designed for human spaceflight with enhanced reliability and safety systems. It is a three-stage vehicle standing 53 meters tall, weighing 640 tonnes, and capable of carrying 10 tonnes to low Earth orbit (LEO). Key upgrades include a human-rated design and the integration of a Crew Escape System (CES), which can safely eject the Crew Module in the event of an anomaly during ascent. LVM3 ASSEMBLY BEGINS: Isro began stacking the nozzle-end segment of the S200 solid rocket motor on Wednesday, officially launching the HLVM3-G1 campaign. The S200 motors are undergoing assembly, while the L110 liquid stage and C32 cryogenic stage are ready for integration at the launch complex. Meanwhile, the Crew Module is being integrated at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), and the Service Module at the U.R. Rao Satellite Centre (URSC). The Orbital Module’s final integration and testing will follow at URSC, Bengaluru. The HLVM3-G1 mission is critical for testing the human-rated systems in an uncrewed environment. The Crew Module features advanced safety margins, multiple redundancies, and re-entry technologies validated through the LVM3-X/CARE mission. This data will be instrumental in ensuring the success of future manned missions. Isro’s legacy in developing heavy-lift launch vehicles has been pivotal for India’s space ambitions. The insights from earlier missions have guided the design of the Gaganyaan spacecraft, with lessons from pad abort tests, air-drop experiments, and system evaluations ensuring readiness for human spaceflight. The maiden Gaganyaan flight will also contribute to India’s long-term vision of building the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS). About Gaganyaan Mission: Gaganyaan is a mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Under the Gaganyaan schedule: Three flights will be sent into orbit. There will be two unmanned flights and one human spaceflight. The Gaganyaan system module, called the Orbital Module will have three Indian astronauts, including a woman. It will circle Earth at a low-earth-orbit at an altitude of 300-400 km from earth for 5-7 days. Payloads: The payload will consist of: Crew module - spacecraft carrying human beings. Service module - powered by two liquid propellant engines. It will be equipped with emergency escape and emergency mission abort. Launch: GSLV Mk III, also called the LVM-3 (Launch Vehicle Mark-3,) the three-stage heavy lift launch vehicle, will be used to launch Gaganyaan as it has the necessary payload capability. Training in Russia: In June 2019, the Human Space Flight Centre of the ISRO and the Russian government-owned Glavkosmos signed a contract for the training, which includes Russian support in the selection of candidates, their medical examination, and space training. The candidates will study in detail the systems of the Soyuz manned spaceship, as well as be trained in short-term weightlessness mode aboard the Il-76MDK aircraft. The Soyuz is a Russian spacecraft. The Soyuz carries people and supplies to and from the space station. The Il-76MDK is a military transport plane specially designed for parabolic flights of trainee astronauts and space tourists. Significance: It will help in enhancement of science and technology levels in the country and help inspire youth. Gaganyaan will involve numerous agencies, laboratories, disciplines, industries and departments. It will help in improvement of industrial growth. Recently, the Government has announced a new organisation, IN-SPACe, part of reforms to increase private participation in the space sector. It will help in development of technology for social benefits. It will help in improving international collaboration. One International Space Station (ISS) put up by multiple countries may not be enough. Regional ecosystems will be needed and Gaganyaan will focus on regional needs: food, water and energy security. IN SHORT: The HLVM3 is an evolution of the LVM3 rocket It has been specifically designed for human spaceflight It is a three-stage vehicle standing 53 meters tall |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
IN A first, a team of scientists from the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Region and National Institute of Ocean Technology imaged an active hydrothermal vent located at a depth of 4,500 m in the Central and South West Indian Ridges in Southern Indian Ocean. Hydrothermal vents: Hydrothermal vents, largely found near tectonic plates, are underwater springs where cold water (about 2 degrees Celsius) prevailing near the seabed comes in close contact with magma in a tectonically active region. When this cold water trickles through fissures on the ocean crust and admixtures with magma, it can turn into super hot water (up to 370 degrees Celsius) and emerge as plumes, rich in minerals and gases, through chimneys and vents. About Hot Spring: A Hot Spring, also known as a geothermal spring is a naturally occurring spring of water that emerges due to heated groundwater. The heat produced is either through the magma within the Earth’s crust or through the movement of fault in the crust. Key Facts on Hot Spring: A Hot Spring is a naturally occurring spring of water that is hotter than 98 degrees Fahrenheit (36.7 degrees Celsius) when it flows from the ground The temperature of this water remains high even during the winter season when the land is covered with ice and snow Hot Spring can be used by human beings for various purposes, based on their temperature There are minerals present in the water released by Hot Spring Hot springs often host communities of microorganisms adapted to life in hot, mineral-laden water. These include extremophile that thrives at high temperature What is Geyser – Hot Spring? A jet of steam and hot water that immediately spouts out of the ground is known as Geyser. It results from the heating of groundwater by shallow bodies of magma. As water is ejected from geysers and is cooled, dissolved silica is precipitated in mounds on the surface. This material is known as sinter. What are Mud Pots – Hot Spring? When the water in a hot spring mixes with dirt or clay before it reaches the surface, the spring is called a mud pot How is Hot Spring Formed? When the rainwater or the groundwater heats upon coming in contact with the rocks that have been heated by magma, deep beneath the Earth’s surface, Hot Spring is formed. This form of geothermal spring generally occurs in areas near volcanic activities. Formation of hot spring is also possible in areas with no volcanic activities. This happens when rainwater flows into the ground and is heated by the radioactive decay of elements present in the rocks and soils that it flows through. How Hot Spring is useful for Human Beings? Hot Springs are tourist attractions in countries where they are present Due to the presence of dissolved minerals in the water formed through Hot Spring, it also holds therapeutic uses. It also has medical attributes Many Hot Springs have been converted into rehabilitation centers for disabled persons Also, beneficial for animals during the extremely cold season. As animals find heat near these sprouts. How is Geothermal Spring dangerous? However, not all Hot Springs can be used for human purposes due to their high temperature, which is not suitable for living beings. Also, the naturally occurring chemical in springs close to volcanic activities can cause severe burns on the skin. Hot Springs In India: India comprises numerous natural hot water springs which have naturally emerged from the geothermal forces beneath the Earth’s surface. With dissolved chemicals and medicinal properties, Hot Springs are present in various parts of the country. Given below are a few of the springs in India:
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
Space startups in Japan and India had agreed to jointly study using laser-equipped satellites to remove debris from orbit, an experimental approach to the increasingly imminent problem of orbital congestion. Tokyo-based Orbital Lasers and Indian robotics company InspeCity would study business opportunities for in-space services such as de-orbiting a defunct satellite and extending a spacecraft’s life. What is Space Debris? It is defined as all non-functional, artificial objects, including fragments and elements thereof, in Earth orbit or re-entering into Earth’s atmosphere. Out of 35,150 tracked objects in orbit, only about 25% are working satellites. (United Nations University) Current Status of Space Debris: Space debris: As per ESA's Space Environment Report 2022, over 30,000 pieces of space debris have been recorded and are being tracked on a regular basis by space surveillance networks. Micro debris: It is estimated that there are approximately 200,000 pieces ranging in size from 1 to 10 cm, with millions more smaller than 1 cm. In addition to this, there are about 34,000 objects greater than 10 cm Growth of satellite constellations: There were approximately 6,718 active satellites orbiting the Earth in 2022, an increase of nearly 2,000 satellites in just one year. Concerns related to Space Debris: Threat to space exploration: Debris collisions can disable an operational spacecraft and damage components like optics and solar panels. E.g. collision with a 10-cm object would cause catastrophic fragmentation of a satellite. Kessler syndrome: Uncontrolled growth of debris can lead to self-sustained cascading collisions creating a chain of reactions. Risk to life on Earth: Large space debris that reenter the atmosphere in an uncontrolled way can create risks for the population on the ground. Space pollution: The accumulation of space debris in Earth's orbit contributes to long-term orbital pollution, which not only complicates space activities but also raises environmental concerns for future generations of space explorers. Tensions between countries: With the increased participation of countries in space activities, disagreements may arise over who is responsible for reducing space debris and who is responsible for paying damages when spacecraft from different countries collide. For instance, the United States accused Russia of endangering the ISS following an anti-satellite weapons test. What are the Initiatives to Deal with Space Debris? India: In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris. ISRO also carried out 21 collision avoidance manoeuvres of Indian operational space assets in 2022 to avoid collisions with other space objects. ISRO has also set up a Centre for Space Debris Research to monitor and mitigate the threat of space debris. ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites. Debris-Free Space Missions by Indian space actors by 2030 Global: The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), an international governmental forum, was established in 1993 to coordinate efforts between spacefaring nations to address the issue of space debris. The United Nations has established the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) to develop guidelines for the long-term sustainability of outer space activities, including the mitigation of space debris. RemoveDEBRIS Mission: for active debris removal (ADR) technology demonstrations. LignoSat: A wooden satellite crafted from magnolia wood to combat space debris. UN Liability Convention (Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Object), 1972 UN Registration Convention (Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space), 1976 The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched the Clean Space initiative, aimed at reducing the amount of space debris and promoting sustainable space activities. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Useful information for all competitive exams:
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO): Formed: 15 August 1969 Preceding agency: INCOSPAR (1962–1969) Headquarters: Bengaluru, Karnataka Chairman: S. Somanath (10th Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation) Primary spaceports: Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Thumba Equatorial Rocket Launching Station, Kulasekarapattinam Spaceport Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA): Formed: 1 October 2003 Headquarters: Chōfu, Tokyo, Japan Administrator: Hiroshi Yamakawa |
||||||||||||||||||
| Important Days | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
Good Governance Week 2024 will be held from December 19 to December 24, 2024. A key part of this national initiative is the Prashasan Gaon Ki Ore campaign, which will take place across over 700 districts, states, and union territories in India. The campaign focuses on addressing public grievances. Key Points: The campaign will be held in 700+ districts from 19.12.2024 to 24.12.2024. All Chief Secretaries, AR secretaries and DCs/DMs of all States/UTs have been invited in the virtual launch function. Secretary, DARPG; Chief Secretary, Govt. of Maharashtra; Chief Secretary, Govt. of Madhya Pradesh; Chief Secretary, Govt. of Assam and Pr. Secretary, Administrative Reforms, Bihar will address the inaugural webinar to formally launch the campaign. More than 700 Districts across the nation will also organize workshops on Good Governance Practices and improvement of Service Delivery. The Prashashan Gaon ki Ore guidelines have been shared with all the Districts and States/UTs. The States/UTs will conduct the following activities during the Prashashn Gaon Ki Ore campaign between December 19th to 24th, 2024: 1. Public grievances redressed in Special Camps 2. Public grievances redressed in CPGRAMS 3. Public grievances redressed in the State portals 4. Service Delivery applications disposed 5. Collation and dissemination of Good Governance practices 6. Success stories on resolution of public grievances Note: Good Governance Day is observed on December 25th every year to commemorate the birth anniversary of Atal Bihari Vajpayee and promote transparency and accountability in governance. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
<< 18-Dec-24
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|







