TSPSC Current Affairs
| ఆర్థిక అంశాలు (Economics) |
|---|
|
|
|
2023-24 గృహ వినియోగ వ్యయం సర్వే (HCES) ముఖ్యమైన ట్రెండ్లను మరియు భారతదేశ ఆర్థిక స్థితిని ప్రతిబింబిస్తుంది.
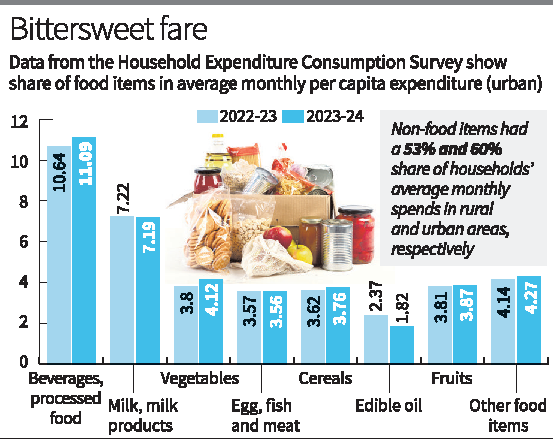
ముఖ్యాంశాలు: గృహ వినియోగంలో పెరుగుదల: ఆగస్టు 2023 నుండి జూలై 2024 వరకు, గత సంవత్సరంతో పోల్చితే, వ్యక్తిగత ప్రాతిపదికన గృహ వినియోగ వ్యయం 3.5% వాస్తవ పెరుగుదల చూపించింది. ఇది వినియోగ అసమానతల తగ్గింపును మరియు పట్టణ-గ్రామ అంతరాలను తగ్గించడాన్ని సూచిస్తుంది. నెలవారీ వ్యక్తిగత వినియోగ వ్యయం (MPCE): గ్రామీణ MPCE: ₹2,079కి 3.53% పెరుగుదల. పట్టణ MPCE: ₹6,996కి 3.48% పెరుగుదల. పట్టణ-గ్రామీణ గ్యాప్: 2022-23లో 71% నుండి **2023-24లో 70%**కి తగ్గింది (2011-12లో ఇది 84%). వినియోగ ధోరణులు: అహారేతర వ్యయాలు: గ్రామీణ ప్రాంతాల్లో 53%, పట్టణ ప్రాంతాల్లో 60% ప్రధాన భాగంగా ఉన్నాయి. తినేవంగడాలు వంటి వస్తువులపై వ్యయం తగ్గడం వల్ల ఆహార వస్తువుల వ్యయం లో కొంత తగ్గుదల. వినియోగ అసమానతలు: జిని గుణాంకం (అసమానత కొలమానం): గ్రామీణ ప్రాంతాలు: 0.266 (2022-23) నుండి **0.237 (2023-24)**కి తగ్గింది. పట్టణ ప్రాంతాలు: 0.314 (2022-23) నుండి **0.284 (2023-24)**కి తగ్గింది. జనాభాలో దిగువ 5%-10% వర్గం అత్యధిక MPCE పెరుగుదలను చూసింది. పేదరికం మరియు ద్రవ్యోల్బణం పై ప్రభావం: సర్వే ద్వారా కొనుసెము ధరల సూచిక (CPI) కోసం గణాంకాలను నవీకరించబడింది, ఇది పేదరిక స్థాయిలను అంచనా వేయడానికి మరియు చిన్నరేటు ద్రవ్యోల్బణాన్ని ట్రాక్ చేయడానికి ఉపయుక్తంగా ఉంటుంది. సర్వే కవరేజ్: 2,61,953 కుటుంబాలు సర్వే చేయబడగా, 59% గ్రామీణ ప్రాంతాల నుండి. ప్రాధాన్యత: ఈ ఫలితాలు ఆర్థిక సమానత్వంలో మెరుగుదల, పట్టణ-గ్రామీణ వినియోగ స్థాయిల మధ్య తేడా తగ్గుముఖం పట్టడం చూపిస్తున్నాయి. గ్రామీణ వినియోగ సహనశీలతను మరియు అహారేతర ఖర్చుల పెరుగుదలపై దృష్టి సారిస్తోంది. జిని గుణాంకం తగ్గడం ఆర్థిక అసమానతల తగ్గింపునకు సంకేతం. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ENGLISH
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) 2023-24The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) findings for 2023-24 reveal important trends in India's economic well-being and consumption patterns:Key Highlights: Increase in Household Consumption: Average household consumption expenditure on a per capita basis rose 3.5% in real terms from August 2023 to July 2024 compared to the previous year. This indicates reduced consumption inequality and a narrowing urban-rural gap. Monthly Per Capita Expenditure (MPCE): Rural MPCE: Increased by 3.53% to ₹2,079. Urban MPCE: Grew by 3.48% to ₹6,996. The urban-rural gap in MPCE declined further to 70% in 2023-24 from 71% in 2022-23 and 84% in 2011-12. Consumption Patterns: Non-Food Items: Account for the majority of expenditure, with a 53% share in rural and 60% in urban areas. Decline in spending on edible oils offset higher spending on items like vegetables amid high food inflation. Consumption Inequality: Gini coefficient (a measure of inequality): Rural areas: Declined from 0.266 (2022-23) to 0.237 (2023-24). Urban areas: Declined from 0.314 (2022-23) to 0.284 (2023-24). The bottom 5%-10% of the population saw the highest increase in MPCE in both rural and urban areas. Poverty and Inflation Insights: Findings contribute to updating the Consumer Price Index (CPI), aiding in poverty estimation and tracking retail inflation trends. Survey Coverage: Data collected from 2,61,953 households across India, with 59% from rural areas. Significance: The results reflect improvements in economic equity, narrowing disparities between urban and rural consumption levels. They emphasize the resilience of rural consumption and the growing focus on non-food expenditure. The decline in the Gini coefficient underlines a reduction in income inequality. This survey is critical for policymakers to design welfare programs, fine-tune inflation measures, and assess the socio-economic impact of government schemes. 
|
| >> More TSPSC Current Affairs |
