SSC Current Affairs
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Polity and Governance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
The Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, Harivansh, rejected the Opposition’s no-confidence motion against Chairman Jagdeep Dhankhar. He said in his ruling that the notice was an act of impropriety to mar the reputation of the Vice-President. The reasons for rejection included a wrong spelling of Mr. Dhankhar’s name in the notice. Constitutional Provisions: The no-confidence notice under Article 67(b) of the Constitution was not addressed to any specific authority. “Invoked Article 67(b) peremptorily mandates at least 14 days’ prior notice for any resolution contemplating the Vice-President’s removal. Vice President in India: The Vice President of India is the second-highest constitutional office in the country after the President of India. The Vice-President is accorded a rank next to the President in the official warrant of precedence. This office is modeled on the lines of the American Vice-President. The Vice President's main role is to act as the President if the President cannot perform his or her duties, such as due to death, resignation, or impeachment. The Vice President also serves as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States), the upper house of the Indian Parliament. How is the Vice President of India elected? The Vice-President, like the president, is elected not directly by the people but indirectly. He is elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both houses of Parliament. Thus, this electoral college is different from the electoral college for the election of the President in the following two respects: It consists of both elected and nominated members of the Parliament (in the case of the President, only elected members). It does not include the members of the state legislative assemblies (in the case of the President, the elected members of the state legislative assemblies are included). Vice-President’s election, like that of the President’s election, is held in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote, and the voting is by secret ballot. All doubts and disputes concerning the election of the Vice-President are inquired into and decided by the Supreme Court, whose decision is final. Vice President of India Constitutional Provisions:
To be eligible for election as Vice-President, a person should fulfill the following qualifications: He should be a citizen of India. He should have completed 35 years of age. He should be qualified for election as a member of the Rajya Sabha. He should not hold any office of profit under the Union government or any state government or any local authority, or any other public authority. Conditions of Office: The Constitution lays down the following two conditions of the Vice-President’s office: He should not be a member of either House of Parliament or a House of the state legislature. If any such person is elected Vice-President, he is deemed to have vacated his seat in that House on the date on which he enters upon his office as Vice-President. He should not hold any other office of profit. Term and Vacancy: Term: The Vice-President holds office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters his office. However, he can resign from his office anytime by addressing the resignation letter to the President. The Vice-President can hold office beyond his term of five years until his successor assumes charge. He is also eligible for reelection to that office. He may be elected for any number of terms. Vacancy: A vacancy in the Vice-President’s office can occur in any of the following ways: On the expiry of his tenure of five years By his resignation On his removal By his death Otherwise, for example, when he becomes disqualified to hold office or when his election is declared void. If the office falls vacant by resignation, removal, death, or otherwise, then an election to fill the vacancy should be held as soon as possible(within six months for President) after the occurrence of the vacancy. What is the procedure for the removal of the Vice President of India? The Vice President can also be removed from office before the completion of his term. A formal impeachment is not required for his removal. He can be removed by a resolution passed by a majority of all the then members of the Rajya Sabha (Effective Majority) and agreed to by the Lok Sabha (Simple Majority). This means that this resolution should be passed in the Rajya Sabha by an effective majority and in the Lok Sabha by a simple majority. It must be noted here that the effective majority in India is only a type of special majority and not a separate one. Further, this resolution can be introduced only in the Rajya Sabha and not in the Lok Sabha. But, no such resolution can be moved unless at least 14 days advance notice has been given. How can the office of the Vice President of India be compared to that of the Vice President of the USA?
The powers and functions of the Vice-President include He is the ex-officioChairman of Rajya Sabha. In this capacity, his powers and functions are similar to those of the Speaker of Lok Sabha. In this respect, he resembles the American vice president, who also acts as the Chairman of the Senate–the Upper House of the American legislature. He acts as President when a vacancy occurs in the office of the President due to his resignation, impeachment, death, or otherwise. He can act as President only for a maximum period of six months, within which a new President has to be elected. Further, when the sitting President cannot discharge his functions due to absence, illness, or any other cause, the Vice-President discharges his functions until the President resumes his office. While acting as President or discharging the functions of the President, the Vice-President does not perform the duties of the office of the chairman of Rajya Sabha. During this period, those duties are performed by the Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha. Vice President of India Significance: The Vice President of India serves as the ex-officio Chairman of the Rajya Sabha, the upper house of the Indian Parliament. As Chairman, the Vice President presides over the sessions of the Rajya Sabha, maintains order and decorum in the chamber, and ensures that the rules and procedures of the house are followed. Though he is not a member of the house, the Vice President can vote in the Rajya Sabha in the case of a tie. The Vice President also appoints the Chairman and members of the Rajya Sabha's various committees. Consideration of motion of removing supreme court or high court judge depends upon the chairman of Rajya Sabha. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Previous Year Questions (PYQs):
Q) Consider the following statements: (2013) 1. The Chairman and the Deputy Chairman of the Rajya Sabha are not the members of that House. 2. While the nominated members of the two Houses of the Parliament have no voting right in the presidential election, they have the right to vote in the election of the Vice President. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Ans: b Vice President of India Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): Q1. Which Vice Presidents later became President in india? Ans: Dr S Radhakrishnan, Dr Zakir Hussain, V V Giri, R Venkataraman, Dr Shankar Dayal Sharma, K R Narayanan are the persons who were first elected as Vice-President and later became the country's President. Dr S Radhakrishnan,Dr Zakir Hussain, V V Giri, R Venkataraman, Dr Shankar Dayal Sharma, K R Narayanan. Q2. Who presides over the sessions of Rajya Sabha in the absence of the Vice President? Ans: The Deputy Chairman, who is elected from amongst the house's members, takes care of the day-to-day matters of the house in the absence of the Chairman. Chairman nominates the panel of chairpersons who preside in the absence of Chairman and Deputy Chairman of Rajya Sabha. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Economy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
Smartphones are now the fourth-largest export item from India with 42 per cent growth to $15.6 billion in FY24, up by one notch in the ranking from the preceding year. India started collecting data for smartphones separately from April 2022. While India’s top export items are dominated by petroleum products, smartphones replaced motor gasoline to become the fourth-largest exported commodity in FY24. Smartphone Exports: According to commerce department data, the spike in smartphone exports was driven by a 158 per cent increase in shipments to the US at $5.6 billion, followed by the United Arab Emirates ($2.6 billion), the Netherlands ($1.2 billion), and the UK ($1.1 billion). The value of mobile devices produced in India for both export and domestic markets in FY24 soared to Rs 4.1 trillion ($49.16 billion), up at least 17 per cent year-on-year (Y-o-Y), according to preliminary estimates by the Indian Cellular and Electronics Association (ICEA), which represents most of the mobile players in the country. 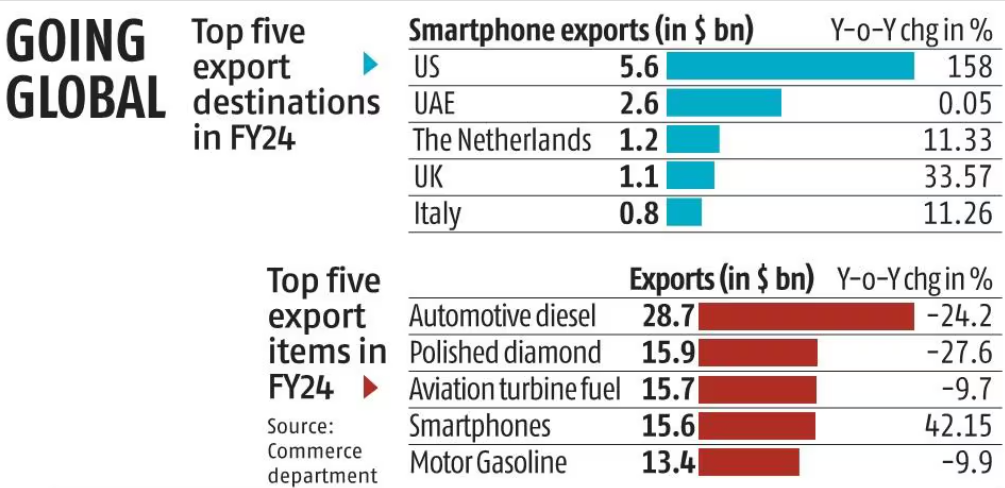 Production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme: Smartphones have been a key success story of the government’s production-linked incentive (PLI) scheme, helping India become the second-largest mobile phone manufac-turing country, after China. It has also been a key instrument in the China-Plus-One strategy, which is focused on leveraging the geopolitical tensions between that country and the US to woo companies manufacturing in China and persuade them to shift to India. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Culture | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
The 10th International Forest Fair, held in Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, commenced on December 17, 2024, and will run until December 23. International Forest Fair Focus Areas: This fair focuses on promoting sustainable forest practices, empowering local communities, and fostering collaboration among various stakeholders in the forestry sector. The event provides a platform for government officials, traders, producers, scientists, and policymakers to engage in meaningful discussions and knowledge exchange. Theme of the Fair: This year’s theme is Women Empowerment through Minor Forest Produce. The theme marks the role of women in managing minor forest produce, which constitutes 50% of the workforce in this sector. The fair aims to promote gender equality and support women’s contributions to the economy. Health Services Offered: The fair includes free medical consultations from qualified Ayurveda doctors. An OPD service is available daily, allowing attendees to access health advice and treatments. This initiative promotes holistic health and well-being, aligning with the fair’s focus on sustainable living. Participation and Collaboration: Encourages collaboration among government bodies, NGOs, and private enterprises. International participation fosters the exchange of best practices in forest management. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
India and France on 19th December signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for the development of the new National Museum, on the lines of the Louvre in Paris, at the historic North Block and South Block in the national capital. Key Takeaways: The museum, named Yuga Yugeen Bharat, when completed would be the largest in the world. The agreement was signed by Herve Barbaret, Director General and CEO of France Museums, and B.R. Mani, Director General of the National Museum of India. The ‘Yuga Yugeen Bharat’ museum will be developed through adaptive reuse in collaboration with France, which is renowned for its expertise in such projects — exemplified by the Louvre, the Grand Palais, and the Hotel de la Marine. Union Minister for Culture & Tourism, Shri Gajendra Singh Shekhawat, expressed the vision behind the project: 📍“This landmark partnership with France will transform the Yuga Yugeen Bharat National Museum into a global beacon of India's rich cultural heritage. Serving as a shining beacon of India's rich and vibrant heritage, the YYBNM is poised to illuminate the journey toward a progressive and inclusive future. Far beyond the traditional idea of a museum, it will redefine the cultural experience by celebrating diversity, fostering inclusivity, and amplifying the voices of our communities. This iconic institution will not only honour India's timeless legacy as the cradle of democracy but also inspire generations to come by bridging the past, present, and future in a powerful narrative of Modern India.” 📍The museum will serve as a global cultural landmark by combining India’s deep-rooted cultural legacy with France’s expertise in museum management and design. Its development will breathe new life into the historic North and South Blocks, preserving their unique architectural features while reimagining their purpose. 📍This initiative also reaffirms India’s commitment to sustainable and adaptive reuse, ensuring the efficient use of space while honouring India’s built heritage and historical traditions. 📍The Yuga Yugeen Bharat National Museum will redefine the museum experience, offering a platform that celebrates India’s heritage while embracing contemporary narratives. Through this collaboration, India and France continue to strengthen their cultural bonds, setting a benchmark for international partnerships in heritage preservation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sports | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
The International Cricket Council on December 19, announced that India and Pakistan will play their matches in ICC tournaments at neutral venues till 2028. The deal was announced by the ICC during the confirmation of hybrid model for Champions Trophy 2025. ICC Statement Key Pointers: Champions Trophy will be played in Pakistan, India matches at neutral venue The 50-over tournament will be played in February-March in 2025 The hybrid model rule will apply for all ICC tournaments hosted by India and Pakistan in 2024-27 cycle Pakistan will not travel to India for Women's World Cup in 2025 and T20 World Cup in 2026 Pakistan have been awarded the hosting rights for Women's T20 World Cup in 2028 As India Today reported, no compensation for Pakistan for losing a part of Champions Trophy hosting rights Key Points to remember: ICC Men’s Champions Trophy 2025 (hosted by Pakistan), set to be played in February and March 2025 ICC Women’s Cricket World Cup 2025 (hosted by India) ICC Men’s T20 World Cup 2026 (hosted by India and Sri Lanka) IN SHORT: India and Pakistan will not travel to each other's countries till 2028 Matches for both teams will be hosted in neutral venues The ICC brokered a deal between the countries on December 19 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Useful information for all competitive exams:
International Cricket Council (ICC): The International Cricket Council (ICC) is the world governing body of cricket. Formation: 15 June 1909 Headquarters: United Arab Emirates Dubai, United Arab Emirates Chairman: Jay Shah (India) (4th Chairman of the International Cricket Council) CEO: Geoff Allardice (Australia) General Manager: Wasim Khan (England) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Kho Kho Federation of India (KKFI) has officially appointed Bollywood superstar Salman Khan as the brand ambassador for the inaugural Kho Kho World Cup, which will be held in New Delhi from January 13 to 19, 2025.
Key Points: The tournament features 24 countries, including the USA, England, Germany, Australia, and Brazil, competing in a league-cum-knockout format for both men’s and women’s teams. Indonesia will send only their women’s team, while others will field both squads. Participating Nations: A diverse lineup of nations will compete in the championship: Africa: Ghana, Kenya, South Africa, and Uganda Asia: Hosts India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Indonesia, Iran, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan, South Korea, and Sri Lanka Europe: England, Germany, the Netherlands, and Poland North America: Canada and the United States South America: Brazil and Peru Oceania: Australia and New Zealand Tournament Structure: The tournament will feature both men’s and women’s divisions, with 12 teams competing in each category. This format ensures intense competition that will highlight the speed, strategy, and sporting excellence intrinsic to Kho Kho. Men’s Division: In the men’s category, the competition will include a strong African presence with Ghana, Kenya, and South Africa. The Asian contingent features hosts India, along with Bangladesh, Indonesia, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan, and South Korea. England and the Netherlands will represent Europe, while North America contributes Canada and the United States. Brazil will represent South America, and Australia completes the 16-team lineup. Women’s Division: The women’s division boasts a competitive set of nations as well. African representatives include Kenya, South Africa, and Uganda. The Asian representation features hosts India, Bhutan, Iran, Malaysia, Nepal, Pakistan, South Korea, and Sri Lanka. European teams consist of England, Germany, and Poland. South America will be represented by Peru, while New Zealand rounds out the women’s bracket. Pakistan’s Dual Participation: Pakistan has secured places in both the men’s and women’s divisions of this inaugural World Cup, further elevating the tournament’s level of competition. Official Tagline: The World Cup’s official tagline, #TheWorldGoesKho, was recently unveiled at a mega event at Thyagraj Stadium. About Kho Kho: Kho Kho is a tag game of India. Its origins are as old as Mahabharata, with strategies and tactics likely derived from Mahabharata itself. The first ever Kho Kho competition was held in the year 1914. In 1959 the first National Championship was held under KKFI was set up in the year 1955. Each kho-kho team has 12 players, but only 9 players from each team play on the field at a time. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
The mascot for the 38th National Games, along with the logo, jersey, anthem, and tagline, was unveiled at Maharana Pratap Sports College in Raipur, Dehradun. Uttarakhand is set to host the National Games from January 28 to February 14, 2025. The event will see over 10,000 athletes, officials, and coaches from across the country, including institutional teams like the Services, competing in 38 sports. 38th National Games 2025 mascot and Logo: The mascot, named “Mauli,” is inspired by the Monal, the state bird of Uttarakhand, symbolizing the region’s uniqueness and encouraging young athletes to aim high. The logo, also inspired by the Monal, highlights the natural beauty and diversity of Uttarakhand. 38th National Games 2025 tagline: The tagline for the Games, “Sankalp Se Shikhar Tak” (From Resolve to Zenith), was also revealed during the event. National Games torch: The ceremonial lighting of the National Games torch marked a key highlight of the event. Symbolizing unity and collective effort, the torch will traverse the state to promote a culture of sports and inspire sportsmanship among the youth. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Important Days | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Why in the news?
The Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB) is to celebrate its 61st Raising Day on December 20, 2024, in Ranidanga, Siliguri. Key Points: 📍SSB comes under the aegis of the Ministry of Home Affairs and a part of the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF), along with six other central security forces in India (Assam Rifles, Border Security Force, Central Industrial Security Force, Central Reserve Police Force, Indo Tibetan Border Police and National Security Guard). 📍It was established as Special Service Bureau in May 1963, in the aftermath of the Chinese aggression in 1962. 📍It was declared a lead intelligence agency for Indo Nepal in June 2001 and assigned the Indo Nepal border. In 2004, it was also assigned Indo Bhutan border. 📍In 2004, SSB received the President’s Colours in recognition of the keystone role in national security, since its inception. Responsibilities: To promote a sense of security among the people living in the border areas. To prevent trans border crimes and unauthorized entry into or exit from Indian territory. To prevent smuggling and other illegal activities on Indian frontiers. 📍It is headquartered in New Delhi and three frontier headquarters are at Lucknow (UP), Patna (Bihar) and Guwahati (Assam). 📍It is spread out on Indo Nepal and Indo Bhutan borders across the states of Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Sikkim, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh. Note: President's Colours: It is the highest honour bestowed upon a regiment in recognition of their contribution to the security of the nation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
<< 19-Dec-24
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|







