Banking Current Affairs
| Deaths |
|---|
|
|
|
Why in News?
Veteran scientist Dr. R Chidambaram, celebrated as the architect of India’s nuclear program and instrumental in the Pokhran nuclear tests of 1974 and 1998, passed away at the age of 88. His contributions to India’s scientific and technological advancements have left an enduring legacy. What are the Key Facts About Dr. R Chidambaram’s Contributions? Background: Dr. Chidambaram, born in 1936, graduated from Presidency College, Chennai, and the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru. Throughout his illustrious career, he held several prestigious positions, including: Director of Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (1990–1993) Chairman of the Atomic Energy Commission and Secretary, Department of Atomic Energy (1993–2000) Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India (2001–2018) Chairman of the Board of Governors, International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) (1994–1995) Key Achievements: Played a critical role in developing India’s nuclear capabilities, particularly through the Pokhran nuclear tests. Spearheaded mega science projects like the National Supercomputing Mission, the quantum technologies mission, and the Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory (LIGO) India project. Established the National Knowledge Network for high-speed connectivity among research institutions and rural technology laboratories. Accolades: Honored with the Padma Shri (1975) and Padma Vibhushan (1999). Received honorary doctorates from multiple universities and was a fellow of eminent science academies worldwide. What is the Significance of His Legacy? Dr. Chidambaram’s work transcended the boundaries of nuclear science. His vision encompassed holistic national progress, integrating scientific advancements with economic growth and security. His leadership in scientific collaboration and policymaking laid the foundation for India’s position as a global scientific leader. Colleagues and peers, including former ISRO Chief K Kasturirangan and ex-CSIR DG Shekhar Mande, praised his grounded nature and ability to inspire across generations. His legacy continues to influence India’s scientific and technological endeavors. Way Forward Build on his vision by supporting mega science projects and fostering collaboration between academia and industry. Continue integrating scientific advancements into national development strategies. Promote innovation in science and technology to uphold India’s global leadership in key areas like nuclear energy, quantum technology, and supercomputing. 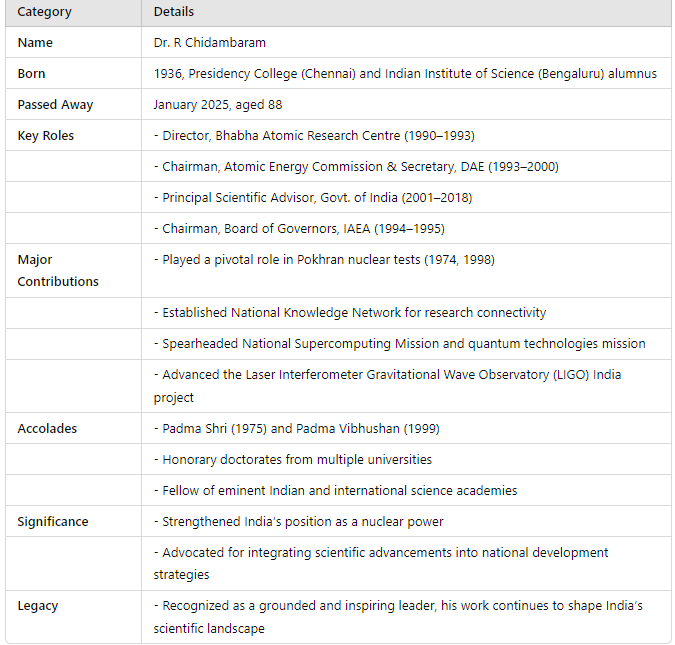
|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in Competitive Exams:
1. Who was Dr. R Chidambaram? A) A former President of India B) A nuclear scientist and architect of India’s nuclear programme C) An ISRO scientist specializing in space missions D) A pioneer of Indian agriculture Correct Answer: B) A nuclear scientist and architect of India’s nuclear programme 2. Which nuclear tests did Dr. R Chidambaram play a key role in? A) Pokhran-I (1974) and Pokhran-II (1998) B) Operation Shakti and Agni-V test C) Kargil War Nuclear Response D) None of the above Correct Answer: A) Pokhran-I (1974) and Pokhran-II (1998) 3. During which years did Dr. Chidambaram serve as the Principal Scientific Advisor to the Government of India? A) 1990–1993 B) 1993–2000 C) 2001–2018 D) 2018–2025 Correct Answer: C) 2001–2018 4. Which prestigious awards did Dr. R Chidambaram receive for his contributions? A) Bharat Ratna and Padma Vibhushan B) Padma Shri and Padma Vibhushan C) Nobel Prize and Padma Shri D) None of the above Correct Answer: B) Padma Shri and Padma Vibhushan 5. What was one of the major mega science projects Dr. Chidambaram supported during his tenure? A) Chandrayaan-3 B) Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory (LIGO) India C) Mangalyaan Mission D) Mission Gaganyaan Correct Answer: B) Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory (LIGO) India |
| >> More Banking Current Affairs |
