Banking Current Affairs
| Economy |
|---|
|
|
|
The Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) findings for 2023-24 reveal important trends in India's economic well-being and consumption patterns:
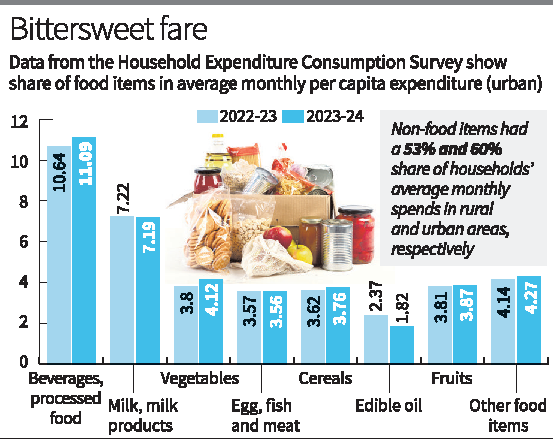
Key Highlights: Increase in Household Consumption: Average household consumption expenditure on a per capita basis rose 3.5% in real terms from August 2023 to July 2024 compared to the previous year. This indicates reduced consumption inequality and a narrowing urban-rural gap. Monthly Per Capita Expenditure (MPCE): Rural MPCE: Increased by 3.53% to ₹2,079. Urban MPCE: Grew by 3.48% to ₹6,996. The urban-rural gap in MPCE declined further to 70% in 2023-24 from 71% in 2022-23 and 84% in 2011-12. Consumption Patterns: Non-Food Items: Account for the majority of expenditure, with a 53% share in rural and 60% in urban areas. Decline in spending on edible oils offset higher spending on items like vegetables amid high food inflation. Consumption Inequality: Gini coefficient (a measure of inequality): Rural areas: Declined from 0.266 (2022-23) to 0.237 (2023-24). Urban areas: Declined from 0.314 (2022-23) to 0.284 (2023-24). The bottom 5%-10% of the population saw the highest increase in MPCE in both rural and urban areas. Poverty and Inflation Insights: Findings contribute to updating the Consumer Price Index (CPI), aiding in poverty estimation and tracking retail inflation trends. Survey Coverage: Data collected from 2,61,953 households across India, with 59% from rural areas. Significance: The results reflect improvements in economic equity, narrowing disparities between urban and rural consumption levels. They emphasize the resilience of rural consumption and the growing focus on non-food expenditure. The decline in the Gini coefficient underlines a reduction in income inequality. This survey is critical for policymakers to design welfare programs, fine-tune inflation measures, and assess the socio-economic impact of government schemes. |
|
|
|
| >> More Banking Current Affairs |
