Banking Current Affairs
TABLE OF CONTENTS |
| National |
|---|
|
|
|
Why in News?
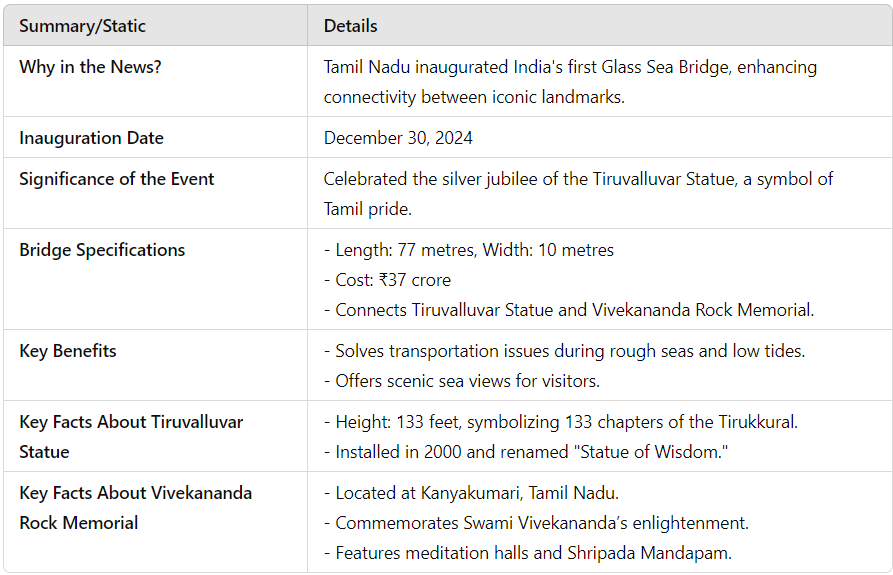
Tamil Nadu has inaugurated India's first glass sea bridge, connecting two iconic landmarks—the Tiruvalluvar Statue and the Vivekananda Rock Memorial in Kanniyakumari. The bridge was unveiled during the silver jubilee celebrations of the Tiruvalluvar Statue. Significance of the Inauguration Chief Minister M.K. Stalin inaugurated the bridge, commemorating 25 years of the Tiruvalluvar Statue, a symbol of Tamil cultural pride and heritage. The bridge enhances connectivity and promotes cultural tourism by enabling seamless access between two major tourist destinations. Key Features of the Glass Sea Bridge Length and Width: The bridge spans 77 meters and is 10 meters wide. Cost: Constructed at a cost of ₹37 crore. Purpose: Provides a pedestrian walkway for visitors to experience panoramic views of the sea. Resolves transportation issues caused by rough seas and low tides. Key Facts About the Tiruvalluvar Statue Inauguration: The statue was unveiled on January 1, 2000, and recently renamed as the Statue of Wisdom. Height: Stands 133 feet tall, symbolizing the 133 chapters of the Tirukkural, a revered Tamil literary work. Cultural Significance: Embodies the philosophy of social justice, encapsulated in the Tirukkural verse: “Pirapokkum ella uyirkkum” (Everyone is equal at birth). Serves as a monumental representation of Tamil identity and heritage. Engineering Feat: Designed by renowned sculptor V. Ganapathi Sthapathi. Weighs 7,000 tonnes and has withstood natural calamities, including the 2004 tsunami. Key Facts About the Vivekananda Rock Memorial Location: Situated 500 meters off the mainland in Kanniyakumari, at the meeting point of the Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean, and Arabian Sea. History: Built in 1970 to honor Swami Vivekananda, who meditated on the rock and attained enlightenment. Architectural Features: Vivekananda Mandapam: A hall dedicated to Swami Vivekananda. Shripada Mandapam: Built to enshrine the footprint of Devi Kanyakumari. Dhyana Mandapam: A meditation hall for visitors. Cultural and Economic Significance Boost to Tourism: The glass sea bridge is expected to draw domestic and international tourists, enhancing the region's tourism potential. Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Highlights Tamil Nadu’s commitment to preserving its rich cultural and historical identity. Infrastructure Development: Sets a benchmark for innovative projects combining tourism and modern engineering. Way Forward Promote Sustainable Tourism: Ensure the bridge and associated infrastructure adhere to environmental and safety standards. Enhance Accessibility: Improve transportation facilities to Kanniyakumari to accommodate increased footfall. Public Engagement: Use the project to educate visitors about Tamil culture and history. Replicate Success: Explore similar infrastructure projects at other cultural and heritage sites across India to boost tourism and preserve history. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in Competitive Exams:
Q1. Consider the following statements regarding Tamil Nadu's glass sea bridge: 1. It connects the Vivekananda Rock Memorial and the Tiruvalluvar Statue. 2. The bridge is 50 meters long and constructed at a cost of ₹30 crore. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 2 only (c) Both 1 and 2 (d) Neither 1 nor 2 Answer: (a) 1 only Q2. The Tiruvalluvar Statue, inaugurated in 2000, represents which of the following? (a) Chapters of the Thirukkural (b) Swami Vivekananda's teachings (c) Tamil Nadu's historical architecture (d) Equality among all living beings Answer: (a) Chapters of the Thirukkural Q3. Which of the following features are unique to the Vivekananda Rock Memorial? 1. It has a Dhyana Mandapam (Meditation Hall). 2. It is located at the meeting point of the Bay of Bengal, Arabian Sea, and the Indian Ocean. 3. It was constructed in 1950 to honor Swami Vivekananda's teachings. Which of the statements given above are correct? (a) 1 and 2 only (b) 2 and 3 only (c) 1 and 3 only (d) 1, 2 and 3 Answer: (a) 1 and 2 only Q4. The glass sea bridge in Tamil Nadu was inaugurated during which significant occasion? (a) Golden Jubilee of Vivekananda Rock Memorial (b) Silver Jubilee of the Tiruvalluvar Statue (c) Centenary celebrations of Tamil Nadu State (d) Inauguration of the Dhyana Mandapam Answer: (b) Silver Jubilee of the Tiruvalluvar Statue |
| Environment |
|
|
|
1. Overview of the Event
On January 3, 2025, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) confirmed that 2024 was India’s warmest year since temperature records began in 1901. The annual mean temperature rose by 0.65°C above normal, surpassing the previous record set in 2016. Globally, 2024 is also expected to be the warmest year, although official announcements are awaited. 2. Factors Contributing to the Record Heat Climate Change: 📍 Accelerated global warming due to human activities. 📍 A consistent increase in temperature over the past decade. El Niño Effect: 📍 A climate pattern marked by the warming of equatorial Pacific Ocean waters. 📍Strong El Niño conditions prevailed from July 2023 to April 2024, impacting global and regional climates. 3. Seasonal Highlights Post-Monsoon (October–December): 📍Recorded the sharpest temperature rise (+0.83°C above normal). Monsoon (June–September): 📍Temperatures were 0.71°C above normal, with excess rainfall (8%) impacting crops and food prices. November 2024: 📍Marked as India’s second warmest November since 1901. 4. Impact on Weather Patterns Rainfall: 📍Northeast monsoon (October–December) was near normal, with some regions experiencing excess rainfall. 📍Extreme rain caused widespread flooding in agricultural regions, reducing food crop output. Winter 2024: 📍Winter was unusually warm, with a muted start. 📍Some regions, like northwest India (Rajasthan, Gujarat), could experience cold day conditions in 2025. 5. Expert Insights Mrutyunjay Mohapatra, IMD Director General: 📍"The annual mean air temperature has shown a consistent rising trend due to climate change. At 0.65°C above normal, 2024 is the warmest year on record." Aarti Khosla, Climate Trends: 📍 "While El Niño played a role, accelerated global warming has been a significant factor since 2016." 6. Global Context Warmest Year for Earth: 📍Between January–November 2024, global air temperatures were more than 1.5°C above normal, breaching the Paris climate summit threshold. Historical Comparison: 📍2016 was the previous record-holder with a global temperature rise of 0.94°C due to a strong El Niño. 7. Future Projections 2025 Outlook: 📍 Above-normal temperatures and weather shocks are likely to continue. 📍IMD predicts warm days and nights for most regions during January–March. Climate Crisis Response: 📍Urgent need for global and national strategies to mitigate the impact of rising temperatures. 8. Key Takeaways 2024 marks a grim milestone as India’s warmest year on record. The combined effects of El Niño and climate change are driving extreme heat and unpredictable weather. Immediate action is needed to address the climate crisis and its cascading impacts on agriculture, water resources, and human health. |
|
|

|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in Competitive Exams:
Q1. With reference to 2024 being India’s warmest year, consider the following statements: 1. The annual mean temperature in 2024 was recorded as 0.65°C above normal. 2. Post-monsoon season (October–December) witnessed the sharpest temperature rise of 0.83°C above normal. 3. 2024 was the second warmest year in India’s recorded history after 2016. Which of the statements given above is/are correct? (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2 only (c) 2 and 3 only (d) 1, 2, and 3 Answer: (b) 1 and 2 only Q2. Which of the following factors contributed to 2024 becoming India’s warmest year on record? (a) Increased rainfall during the southwest monsoon (b) A weak La Niña and its impact on global temperatures (c) A strong El Niño and accelerated climate change (d) Reduced agricultural activity and deforestation Answer: (c) A strong El Niño and accelerated climate change Q3. What role did El Niño play in India’s record temperatures in 2024? (a) Caused above-average rainfall during the northeast monsoon (b) Contributed to higher temperatures by warming the equatorial Pacific Ocean (c) Lowered global air temperatures in early 2024 (d) Reduced India’s monsoon rainfall significantly below normal Answer: (b) Contributed to higher temperatures by warming the equatorial Pacific Ocean Q4. Globally, 2024 breached the 1.5°C warming threshold set by which of the following agreements? (a) Kyoto Protocol (b) Paris Climate Agreement (c) Montreal Protocol (d) United Nations Sustainable Development Goals Answer: (b) Paris Climate Agreement Q5. What is the warmest year on record for both India and the world? (a) 2016 (b) 2020 (c) 2024 (d) 2017 Answer: (c) 2024 |
| Science and Technology |
|
|
|
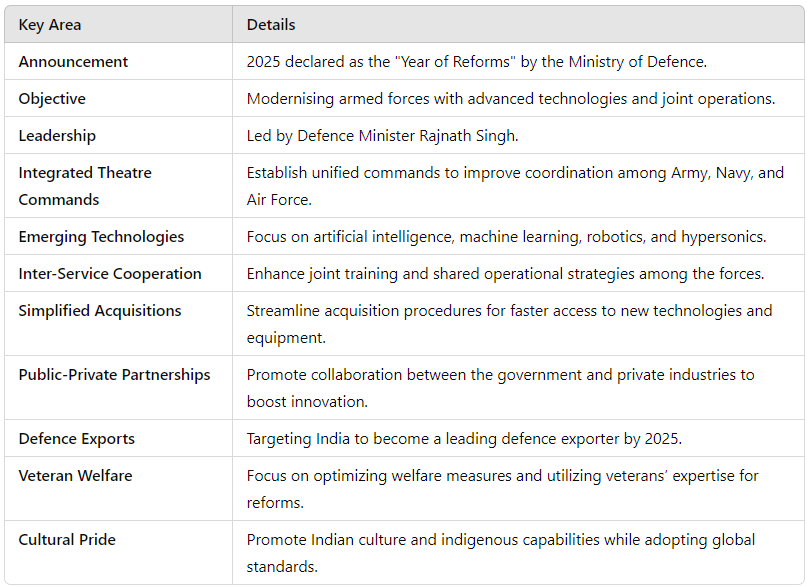
The Ministry of Defence has announced 2025 as the "Year of Reforms", aiming to transform India's defence landscape. Spearheaded by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh, this initiative seeks to modernize the armed forces, enhance joint operations, leverage cutting-edge technologies, and position India as a global leader in defence exports.
Context of the Announcement The declaration comes at a critical juncture, as India confronts evolving security challenges. Modernisation and technological advancements are essential to address these threats effectively. The reforms aim to boost operational readiness and foster seamless collaboration among the Army, Navy, and Air Force. Key Areas of Reform Integrated Theatre Commands Unified commands to improve coordination across the three services. Enhanced operational efficiency and quicker response to threats. Emerging Technologies Focus on artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotics, and hypersonics. Adoption of modern warfare tactics informed by these advancements. Inter-Service Cooperation Joint training exercises and shared operational strategies. Strengthened ability to conduct integrated military operations. Streamlined Acquisition Procedures Simplification of procurement processes for faster access to new technologies and equipment. Boosts readiness and capability. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) Encourages collaboration between the government and civil industry. Promotes innovation and accelerates the modernization of defence systems. Focus on Defence Exports and R&D India aspires to be a global defence exporter by 2025. Enhanced research and development (R&D) and partnerships with international manufacturers. Better integration of resources to drive technological innovation. Veteran Welfare Initiatives Optimising welfare measures for veterans, recognizing their contributions. Utilizing their expertise to drive innovation and policy reforms in the defence sector. Promoting Cultural Pride and Indigenous Capabilities Emphasis on Indian culture and unique defence needs within the armed forces. Developing indigenous technologies while adopting global best practices. Aligning modernization with India’s local conditions and requirements. Key Takeaways Leadership: Rajnath Singh is spearheading the reforms as the current Defence Minister of India. Technological Advancement: AI and robotics are pivotal for future military strategies. Joint Operations: Integrated Theatre Commands will ensure effective collaboration. Global Aspirations: India is positioning itself as a leading defence exporter by 2025. Conclusion The "Year of Reforms" reflects India's ambition to modernize its military and become a global defence powerhouse. With a focus on technology, innovation, and collaboration, these reforms aim to create a modern, self-reliant, and globally competitive defence ecosystem. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in Competitive Exams:
Q1. Who declared 2025 as the "Year of Reforms"? (a) Ministry of Home Affairs (b) Ministry of Defence (c) Ministry of External Affairs (d) Ministry of Finance Answer: (b) Ministry of Defence Q2. What is the main objective of the "Year of Reforms"? (a) Strengthening the economy (b) Enhancing public health systems (c) Modernising the armed forces (d) Boosting education standards Answer: (c) Modernising the armed forces Q3. Which Defence Minister leads the 2025 reforms? (a) Nirmala Sitharaman (b) S. Jaishankar (c) Rajnath Singh (d) Amit Shah Answer: (c) Rajnath Singh Q4. What are Integrated Theatre Commands aimed at? (a) Coordinating military operations among the three armed services (b) Conducting international military drills (c) Acquiring foreign defence technologies (d) Reducing military expenses Answer: (a) Coordinating military operations among the three armed services Q5. Which technologies are prioritized in the reforms? (a) Blockchain and 5G (b) Artificial Intelligence, robotics, and hypersonics (c) Solar and wind energy (d) Quantum computing and blockchain Answer: (b) Artificial Intelligence, robotics, and hypersonics Q6. What is the target for India in the global defence market by 2025? (a) To be a leading defence exporter (b) To reduce imports by 50% (c) To increase foreign military alliances (d) To develop nuclear weapons Answer: (a) To be a leading defence exporter |
| Deaths |
|
|
|
Taxonomy Pioneer K.S. Manilal
K.S. Manilal, a renowned taxonomist and botanist, passed away at the age of 86 in Thrissur, Kerala, after a prolonged illness. Known for his groundbreaking contributions to botany, he was instrumental in translating and annotating the Latin treatise Hortus Malabaricus, opening up its vast botanical knowledge to the modern world. Research and Contributions Hortus Malabaricus Originally authored by Hendrik Adriaan van Rheede, governor of Malabar under the Dutch East India Company (1669–1676). Published between 1678 and 1693 in Amsterdam. Documented 742 plant species from the Malabar Coast, detailing their medico-botanical uses. Manilal dedicated 35 years to translating and annotating the 12-volume work into English and Malayalam. His work brought to light the life, culture, and natural wealth of Kerala, Karnataka, and Goa. Silent Valley Research Conducted extensive studies in the Silent Valley rain forest during the 1980s. His findings contributed significantly to its ecological conservation. Recognition and Awards Padma Shri (2020): For his contributions to botany and taxonomy. Order of Orange-Nassau (Netherlands): For his exceptional research on Hortus Malabaricus. Founder of the Indian Association for Angiosperm Taxonomy. Legacy and Academic Impact Authored 198 research papers and 15 books on taxonomy and botany. Pioneered studies on the medico-botanical, socio-political, and linguistic significance of plants. Served as a professor of botany at the University of Calicut for 23 years (1976–1999). His translations of Hortus Malabaricus were published by the University of Calicut in 2003. Environmental and Historical Contributions Highlighted the importance of preserving biodiversity and cultural heritage. Made Asia’s oldest printed botanical work globally accessible. Key Takeaways Manilal’s work bridged historical and modern botany. His contributions continue to inspire environmental conservation and academic research. Recognized globally for his dedication to scientific and cultural integration. |
|
|

|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in Competitive Exams:
Q1. Who was K.S. Manilal, and what was he renowned for? (A) A poet known for classical works (B) A taxonomist who worked on Hortus Malabaricus (C) A historian who studied ancient India (D) A social reformer in Kerala Answer: (B) A taxonomist who worked on Hortus Malabaricus Q2. What is Hortus Malabaricus best known for? (A) Documenting ancient Indian sculptures (B) Describing plant species and their medicinal properties (C) Analyzing ancient coins from Kerala (D) Studying animal species in Western India Answer: (B) Describing plant species and their medicinal properties Q3. How many plant species are described in Hortus Malabaricus? (A) 500 (B) 742 (C) 650 (D) 820 Answer: (B) 742 Q4. Which prestigious award was conferred upon K.S. Manilal in 2020? (A) Bharat Ratna (B) Padma Shri (C) Sahitya Akademi Award (D) Arjuna Award Answer: (B) Padma Shri Q5. Which country honored K.S. Manilal with the 'Order of Orange-Nassau'? (A) United Kingdom (B) Netherlands (C) Germany (D) France Answer: (B) Netherlands |
| Appointments and Resigns |
|
|
|
On January 1, 2025, Bhuvnesh Kumar, a 1995-batch IAS officer from the Uttar Pradesh cadre, assumed the role of CEO of the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI). He also serves as Additional Secretary at the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY). Kumar succeeds Amit Agrawal, a 1993-batch IAS officer who was recently appointed Secretary, Department of Pharmaceuticals.
UIDAI, which oversees Aadhaar, plays a critical role in India’s digital identity ecosystem, contributing significantly to governance and service delivery. Under Kumar’s leadership, UIDAI is expected to continue driving innovation in Aadhaar services and enhancing its integration into India’s digital infrastructure. Key Highlights 1. Leadership Transition New CEO: Bhuvnesh Kumar took charge as UIDAI CEO on January 1, 2025. Dual Role: Continues as Additional Secretary at MEITY. Predecessor: Amit Agrawal, now Secretary, Department of Pharmaceuticals. 2. Professional Background of Bhuvnesh Kumar Central Government Roles: Additional Secretary and Joint Secretary, MEITY. State-Level Roles in Uttar Pradesh: Principal Secretary, Departments of Animal Husbandry, Dairy Development, and Fisheries. Secretary, Departments of Finance and Technical Education. Divisional Commissioner, Department of Land Revenue. Secretary, Planning, Vocational Education, and Sports & Youth Welfare. 3. Aadhaar Milestones Cumulative Enrolments: Over 1.41 billion individuals registered. Updates and Corrections: 1.07 billion cases processed. Routine Authentications: Over 1.27 billion transactions conducted. e-KYC Verifications: More than 21.8 billion verifications completed. 4. Recent Aadhaar Trends Saturation Point: New enrolments fell below one million for the first time in October 2024. December 2024 Data: Only 9.3 lakh new Aadhaar numbers were generated. Significance of Appointment Kumar’s extensive administrative experience at both state and central levels positions him well to steer UIDAI. Focus areas under his leadership include: Streamlining Aadhaar services. Enhancing digital governance. Expanding the use of Aadhaar for service delivery and authentication. |
|
|

|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) in Competitive Exams:
Q1. Who has been appointed as the CEO of UIDAI on January 1, 2025? (a) Amit Agrawal (b) Bhuvnesh Kumar (c) Rajesh Singh (d) Sanjay Malhotra Answer: (b) Bhuvnesh Kumar Q2. Who did Bhuvnesh Kumar succeed as the CEO of UIDAI? (a) Sanjay Malhotra (b) Amit Agrawal (c) Rajesh Verma (d) Gaurav Gupta Answer: (b) Amit Agrawal Q3. As of 2024, what is the approximate total number of Aadhaar enrolments in India? (a) 1.21 billion (b) 1.41 billion (c) 1.07 billion (d) 1.27 billion Answer: (b) 1.41 billion |
|
<< 1-Jan-25
|
|
|




